
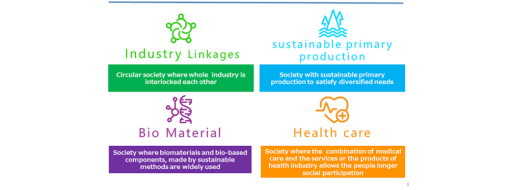
SDGs and Paris Agreement force to change the current society to a sustainable, circular and wellness society, as well as the bio-based society across the globe. Based on these circumstances, the Japanese government has developed the “Japan Bioeconomy Strategy” since 2019 to achieve the world’s most advanced bioeconomy society in Japan by 2030.
The strategy has three featuring points:
Industry, academia, and local governments pursue together the strategy and are able to receive various supports from the related Japanese government ministries as needed. The strategy also points out that even if each company or university individually struggles with biological technologies, the real industrialization is unable to be accomplished, and that bio-communities with strong/unique sciences and technologies are absolutely essential in Japan for effective open innovation.
Furthermore, international collaboration is essential to promote bioeconomy, and there is high potential for creating synergies among states sharing fundamental values. Currently, six bio-communities, two global bio-communities and four local bio-communities with unique sciences and technologies, were certified by the Japanese Government Cabinet Office. Companies based in the EU are also invited to get involved and contribute.
Nine market-segments